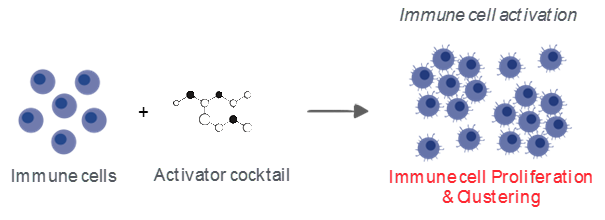
Understanding and modulating the mechanisms underlying activation, proliferation & clustering of immune cells is key for the development of innovative approaches to promote immune cell function and tackle tumor progression.
One of the most common ways to measure immune cell activation in vitro is the assessment of T cell proliferation upon antigen- or TCR-mediated stimulation. In this respect, Explicyte is offering valuable in vitro PBMC- and T cell-based 96-w plate assays to evaluate the effects of immunomodulatory compounds/antibodies alone and in combination with anti-CD3 antibody, on immune cell activation. By live cell time-lapse imaging, treatment effects are evaluated in a kinetic and phenotypic manner on the immune cell proliferation and clustering, as well as functionally on the release of key effector cytokines.