In-house in vivo platform to evaluate & characterize novel immunotherapies
- Syngeneic models: a large panel of immuno-competent tumor-bearing models
- Custom schedules & routes of administration to fit sponsor’s needs
- Documented models: immune response to standard cancer treatments already characterized (including immune checkpoint inhibitors)

Flexible sampling strategy
- Samples collection scheduling adjusted to the MoA of your candidate compound: options to add satellite mice, or perform serial bleeding, intra-tumoral biopsies, microdialysis
- Collection of various sample types: tumor site, fluids (blood, serum, plasma, …), lymphoid organs (spleen, tumor-draining lymph nodes, …)
Versatile technology platforms, & validated tumor & immune markers
- Choice of the most appropriate platform based on the sample nature and the MoA of your compound, including flow cytometry, digital pathology, RNA sequencing, and more.
- Evaluation of immunological markers including specific phenotypic and activation markers, soluble mediators, etc.
- Tailored data analysis to gain insights into the MoA of your compounds
Experts
in Immuno-Oncology
- >10 years of experience in the assessment of tumor and immune markers
- Specific expertise in the analysis of tumor infiltrates and tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS)
- 30+ peer-reviewed publications in key immuno-oncology journals
Personalized
approach
- A dedicated study director (PhD) from experimental plan to final report discussion
- Wide range of validated panels, and development of additional markers on a custom basis

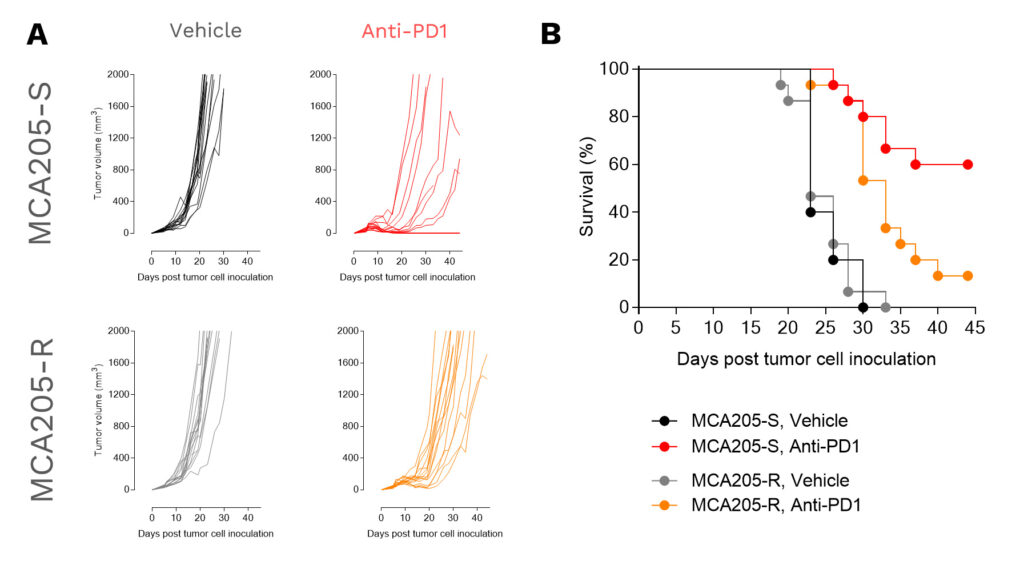
At the 2022 AACR annual meeting, Explicyte presented a poster describing a novel anti-PD1-resistant sarcoma model and its immunological features. In this experimental setting, animals were allocated as either “efficacy” or “satellites” groups, depending on the specific readouts required.
In vivo efficacy study
Individual (A) tumor volume (mm3) and Kaplan-Meier plot survival (B) of MCA205 tumor-bearing mice implanted either with the anti-PD1 sensitive (MCA205-S) or resistant (MCA205-R) tumor cell line, upon vehicle (n=20) or anti-PD1 antibody (n=20) treatments.
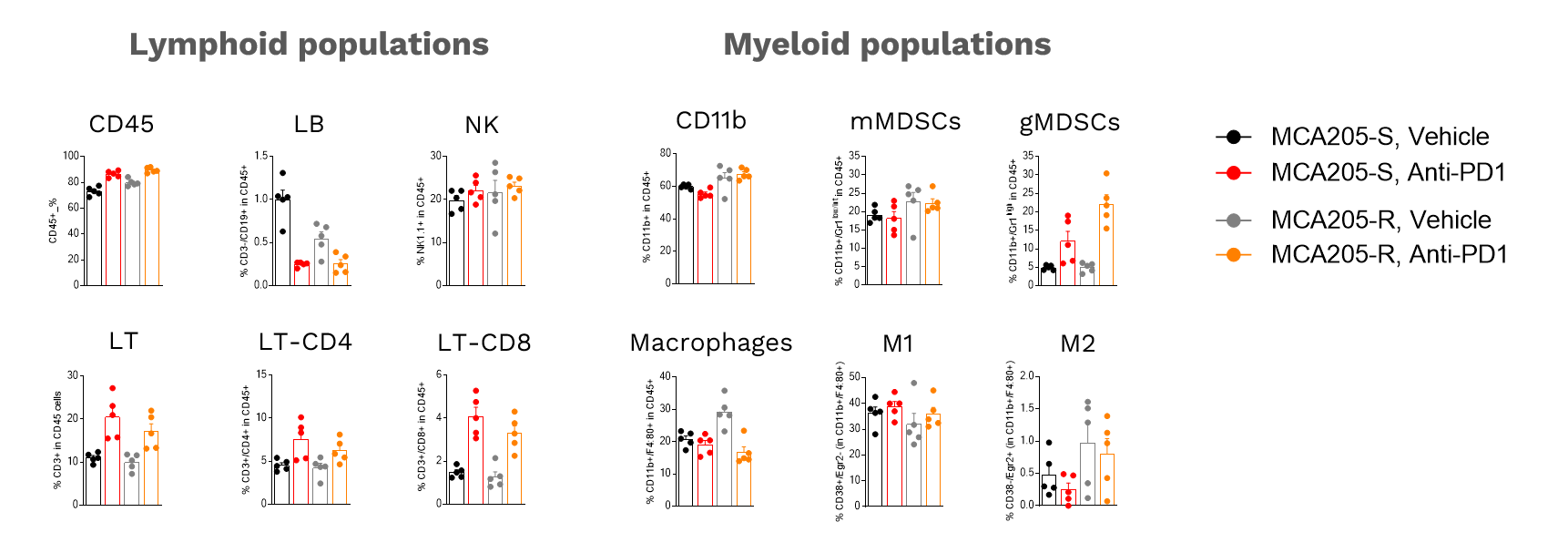
Tumor-Infiltrating Leukocytes (TIL) analysis
Analysis of anti-PD1 MCA205-S and MCA205-R tumor immune cell infiltrate following vehicle (n=5) or anti-PD1 antibody (n=5) treatments. Tumors were retrieved on day 16 post-tumor inoculation and processed for immunostaining and multiparametric flow cytometry. The analysis included markers from both the lymphoid and myeloid lineages, according to a multiplexed panel including CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, NK1.1, CD11b, F4:80, Gr1, CD38, Egr2, and viability markers.
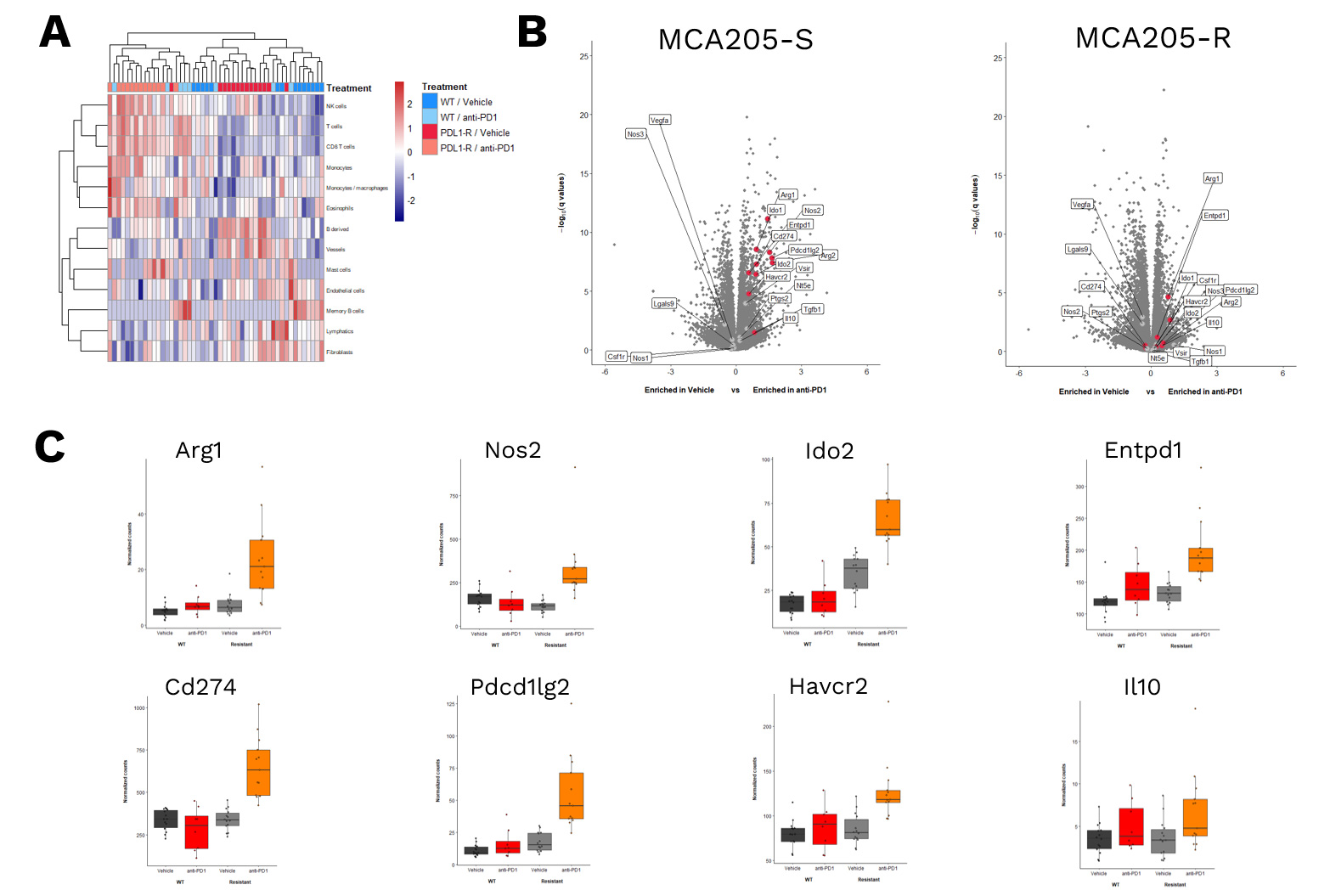
RNA sequencing & gene expression analysis
RNASequencing data of MCA205-S and MCA205-R tumors – collected from either vehicle- or anti-PD1 antibodies-treated mice – were processed for (A) unsupervised analysis of different immune cell susbets, revealing a differential immune cell infiltrate profile based on anti-PD1 sensitivity (S vs R). (B) Volcano plot of gene expression analysis in MCA205-S (left) and MCA205-R (right) tumor samples comparing anti-PD1 vs Vehicle groups. The Y-axis depicts significance while the X axis represents the Log2 fold change between anti-PD1 and vehicle-treated mice. (C) Histogram illustrating gene expression in vehicle and anti-PD1 treated mice for both MCA205-S and MCA205-R models.
Your contacts

Talk to our team !
Paul Marteau, PharmD (preclinical study director), Imane Nafia, PhD (CSO), Loïc Cerf, MSc (COO), Alban Bessede, PhD (founder, CEO), Jean-Philippe Guégan, PhD (CTO)
Tell us about your project !
Immune response profiling for cancer immunotherapies I Preclinical CRO services
Various immunological modulators have the potential to provide an anti-tumor immune-driven response, which is evaluated through in vivo efficacy across valuable and relevant in vivo models, and thus offer promising approaches for cancer therapy. Efficiency of many of these modulators is usually underlied by a strong impact on the immune system which needs to be depicted through relevant models and immunological readouts, in order to see whether the modulation of immune subset responses correlates with the impact of therapeutics on tumor growth in untreated and challenged mice. Notably, depending on their responsiveness degree to different immune checkpoint inhibitors and therapies, tumor models differ in extent and type of immune cell modulation, while the in vivo tumor responses can be similar. Profiling immune cell function permits for building a complete package with in vivo data for a deeper understanding of how a cancer therapy performs. Explicyte has developed and validated a comprehensive panel of tools aiming at evaluating the modulation of the immune system response by novel therapies in syngeneic tumor-bearing mice, in the presence of a functionally immunocompetent system. Profiling of immune function of key cell subsets can be performed both at the tumor site level and in peripheral compartments e.g. blood, spleen, tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs)…, through assaying cell surface markers, cell activation markers, antigen-specific T lymphocyte markers, MDSC (myeloid-derived suppressor cells) markers, cytokines release, and immunological marker-encoding genes, using appropriate methodologies and platforms (e.g. flow cytometry, RT-qPCR, immunohistology-based imaging…). Immune function can be evaluated to delineate a mechanism of action and see how a therapy performs in the presence of a functional immune system where tumor-host immunity interactions are preserved. Standardly, 4 mice are used per experimental group to characterize the immune response underlying anti-tumor effects. Standard package includes 4 experimental groups comprised of 4 mice each exposed to i) vehicle (controls), ii) a reference treatment, iii) a test compound, and iv) test compound combined with the reference treatment. Immune profiling can be performed in 2 compartments; either within the tumor and/or at the periphery (TDLNs, spleen, blood…). Quantitative multiplex immunological analysis is performed by assaying relevant immune markers to address the immune function modulation. Immunological markers including specific antigens, activation markers, and soluble mediators can be evaluated using adapted methodologies with appropriate platforms, e.g. flow cytometry, RT-qPCR, immunohistology-based imaging, ELISA… Validated traditional but also custom marker panels can be generated to address specific program-related needs.