The underlying question: Does your specific tumor antigen-directed antibody display ADCC activity, triggering an immune response to destroy the antibody-coated target cells?
- Format: 96- or 384-well plates
- Model: human tumor cell lines co-cultured with primary NK cells
- Readouts: Tumor cell apoptosis & count by real-time live-cell imaging, and NK cells response via the capture of IFNγ release
- Standards: Trastuzumab (anti-HER2), Cetuximab (anti-EGFR),
- On request: Assessment of cytokine release, assessment of NK cytotoxic factors (perforin/granzymes), proteomics, transcriptomics
Control – 24h post-coculture
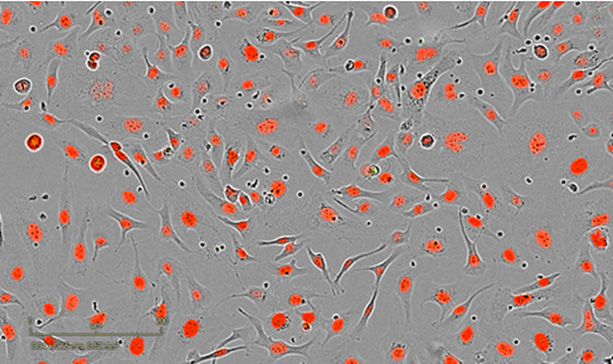
Untreated SKOV3 cells co-cultured with stimulated NKs
Treated– 24h post-coculture
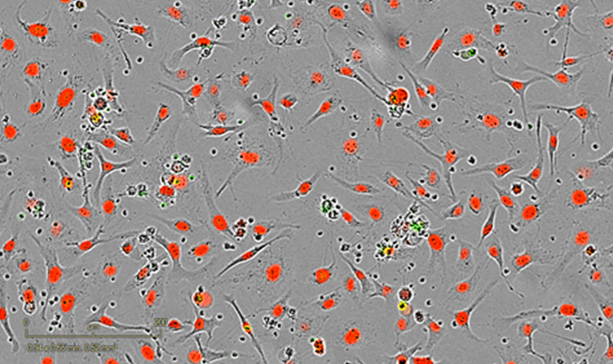
Exposure of cetuximab-challenged SKOV3 cells to stimulated NKs triggers ADCC activity causing apoptotic death of target SKOV3 cells
Assay principle
- Challenge of tumor cells with candidate antibodies, followed by exposure to NK cells
- Parallel capture of the tumor and immune components:
- Real-time monitoring of tumor cell count (nuclear fluorescent probe) and tumor cell death (caspase 3/7 fluorescent reagent)
- Quantification of IFNγ release – surrogate of NK cell response
- Automated image segmentation & analysis
- Additional readouts: immunophenotyping, cytokine release, gene expression, proteomics
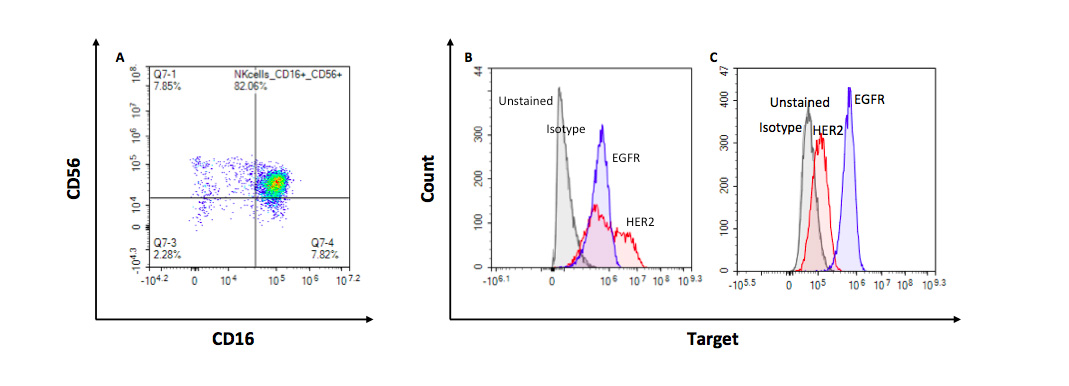
Flow-cytometry-based characterization of NK and target cancer cells for their respective expression of CD16 and intended tumor antigens
Flow cytometry evaluation of the expression of CD16 in CD56+ primary NK cells after their isolation from PBMCs (A), and of HER2 and EGFR target tumor antigens in ovarian SKOV3 (B) and lung A549 (C) tumor cells.
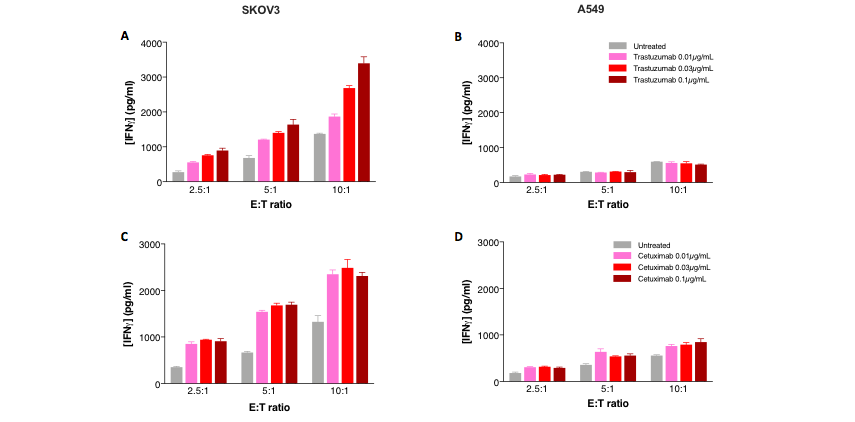
IFNg release by activated NK cells highlights specific anti-HER2 and EGFR antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity
Combination of NK cells and anti-HER2 or anti-EGFR antibodies enhances NK-mediated cytotoxicity in target tumor cells, in a NK ratio-dependent manner. SKOV3 ovarian (HER2+/EGFR+, A, B) and A549 lung (HER2-/EGFR+, B, D) tumor cells were cultured under control, trastuzumab-, or cetuximab-treated conditions and, activated primary NK cells were then added at different E:T ratios. 24h later, supernatants were collected and analyzed for IFN? release as a surrogate of NK-induced cell toxicity. While IFN? levels are increased in a NK ratio-dependent manner, thereby reflecting the basal direct NK cytotoxic activity on both SKOV3 and A549 cells (A-D), cetuximab is shown to promote this activity on both SKOV3 and A549 cells (EGFR+, C, D), while trastuzumab induces ADCC only on SKOV3 cells (HER2+, A).
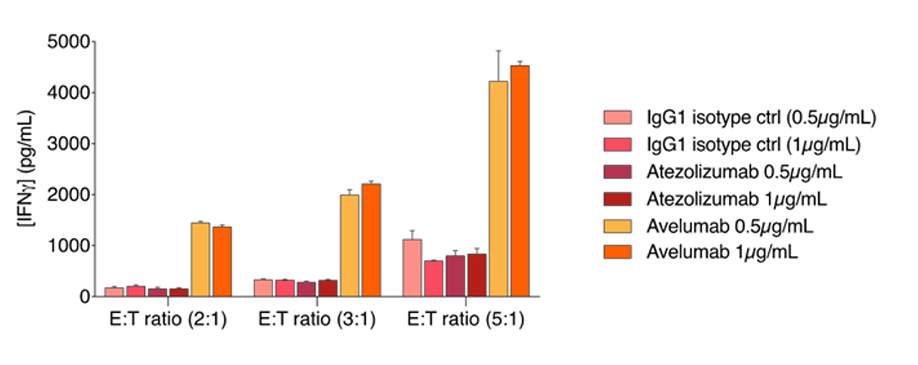
Avelumab triggers NK-mediated ADCC against the TNBC MDA-MB-231 tumor cell line
Avelumab promotes NK response to MDA-MB-231 breast tumor cells, in a NK ratio-dependent manner. MDA-MB-231 tumor cells were cultured under control and Atezolizumab- or Avelumab-treated conditions and, afterwards, activated primary NK cells were added at different E:T ratios. Afterwards, supernatants were collected and analyzed for IFN𝜸 release as a surrogate of NK response function. While IFN𝜸 levels are increased in a NK-ratio dependent manner, only Avelumab further promotes this increase, whatever the E:T ratio.
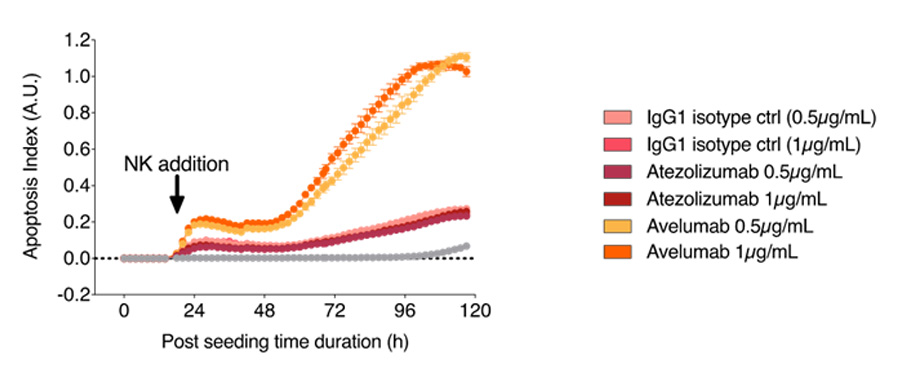
Avelumab enhances NK cytotoxicity toward MDA-MB-231 breast tumor cells. MDA-MB-231 tumor cells were cultured under control and Atezolizumab- or Avelumab-treated conditions and, afterwards, activated primary NK cells were added at an appropriate E:T ratio. Specific tumor cell apoptosis (using a caspase 3/7 probe) was kinetically monitored by live cell imaging, normalized and analyzed. Only Avelumab induces an increase of apoptosis toward tumor cells.
Why working with Explicyte?
Experts
in Immuno-Oncology
- 100+ in vitro campaigns conducted over the past 10 years
- 30+ peer-reviewed publications in key immuno-oncology journals
- A comprehensive technology platform to decipher mechanism of action (activation markers, signaling pathways…)
Personalized
approach
- Targeted discussion based on your request to design bespoke strategy & fit-for-purpose study proposal
- A dedicated study director (PhD level) from experimental plan to final report discussion
- Custom cellular models: over 100 human cancer cell lines available, to be cultured with target primary immune cells
Your contacts

Talk to our team !
Paul Marteau, PharmD (preclinical study director), Imane Nafia, PhD (CSO), Loïc Cerf, MSc (COO), Alban Bessede, PhD (founder, CEO), Jean-Philippe Guégan, PhD (CTO)
Tell us about your project !
ADCC assay I NK cells I Immuno-Oncology CRO services
Consisting in the targeting of cancer cells for destruction by antibodies to be then killed by effector immune cells, antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) is thus the basis of several monoclonal antibody therapies which have been proven powerful and highly promising for cancer treatment. Explicyte offers to perform an ADCC assay based on the full-time course monitoring of both cell proliferation and death of tumor cells, in the presence of immune cells and of candidate antibodies targeting specific tumor antigens. Our kinetic and quantitative cell-based assay allows thus the dynamic assessment and evaluation of the efficacy of test antibodies in eliciting ADCC and directing killing activity towards target tumor cells.