Experts in syngeneic mouse tumor models
- Immuno-competent mouse models
- Subcutaneous or orthotopic implantation of tumor cell lines
- Well-characterized response to immune checkpoint inhibitors or reference chemotherapies (responding & non-responding models)
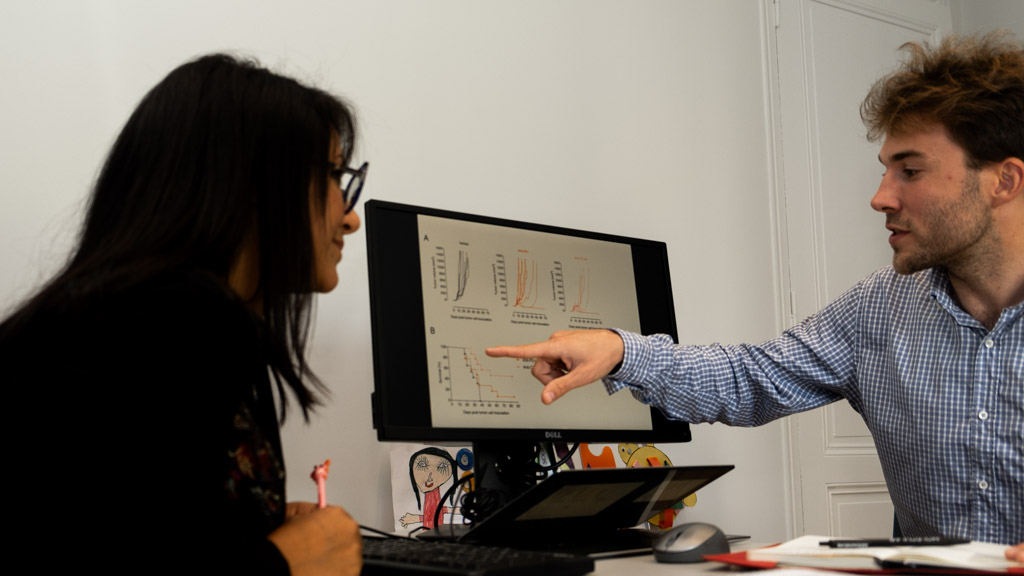

Straightforward in vivo efficacy studies in immuno-oncology
- Flexible administration schedule & route intraperitoneal (IP), intravenous (IV), oral, feeding, subcutaneous, intra-tumoral, intra-muscular, intra-cerebral, …
- Anti-tumor response assessed 3 times per week (tumor size, body weight, survival) throughout follow-up
- On-demand sample collection: blood, serum, plasma, tumor, organs
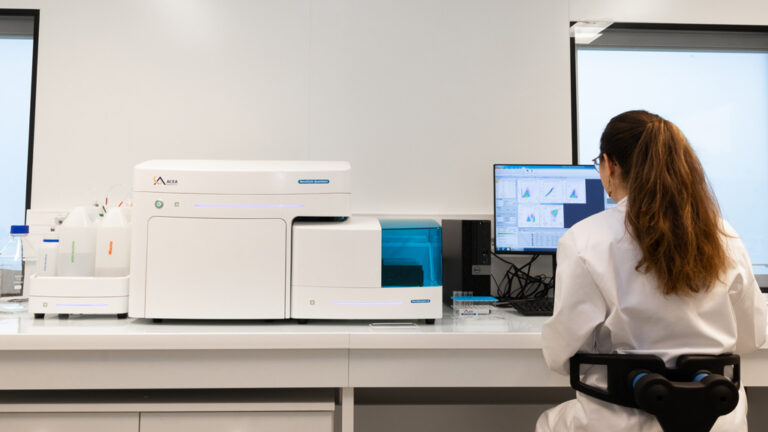

A comprehensive platform to characterize immune response
- Options to monitor immune response over time: satellite mice, serial bleedings, intra-tumoral biopsies, tumor microdialysis
- In-house platform for quantitative & multiplex analysis of immune markers: flow cytometry, digital pathology, spatial transcriptomics, proteomics, …
Why working with Explicyte?
Experts
in Immuno-Oncology
- 150+ in vivo campaigns conducted over the past 10 years
- 30+ peer-reviewed publications in key immuno-oncology journals
- Innovative experimental & analytical strategies custom-tailored to our clients’ projects
A flexible
approach
- A top-level scientist dedicated to each study direction from experimental plan to final report
- Weekly reports to provide regular updates & adapt experimental strategy
- Comprehensive analytical platform to decipher anti-tumor response
Your contacts

Talk to our team !
Paul Marteau, PharmD (preclinical study director), Imane Nafia, PhD (CSO), Loïc Cerf, MSc (COO), Alban Bessede, PhD (founder, CEO), Jean-Philippe Guégan, PhD (CTO)
Tell us about your project !
In vivo models for immuno-oncology I Cancer ImmunoTherapy CRO Services
Testing novel cancer immunotherapies in predictive animal models is a key step for the development of innovative therapeutic approaches acting in conjunction with the host immune system to enhance anti-tumor responses. Syngeneic mouse models provide a comprehensive effective approach for in vivo efficacy studies as well as to underlie mechanism(s) of action and safety profile of candidate immunotherapeutics, in the presence of a functionally immunocompetent system. To assess new compounds for their ability to promote anti-cancer responses, our syngeneic tumor-bearing mouse models, including subcutaneous and orthotopic formats, have been developed and characterized for their response to known chemotherapy and immunotherapy treatments, including TLR3 stimulation and first-in-class immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-CTLA-4, anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1 antibodies). Our models are thus suitable to monitor both efficacy and immunological responses to treatments, associated with different platforms including flow cytometry, RT-qPCR, and microdialysis. To summarize our preclinical CRO services for anti-tumor immune response profiling: key immunological markers can be analayzed within the tumor and in peripheral sites (blood, spleen, lymph nodes) using appropriate quantitative multiplex technologies such as flow cytometry, RT-qPCR, and immunohistochemistry or immunohistofluorescence-based imaging. Finally, Blood or derivatives as well as solid tissue samples can be collected from mice to be then sent to the Sponsor or used in subsequent studies. This way we avoid to re-launch the in vivo part of studies aiming at evaluating the immune response profile across the treatment groups.