-
- Model features: immune cell infiltration – suppressive subsets, suppressive immuno-privileged tumor microenvironment
- Tumor cell line: Luc2-GL261 glioma cells (for bioluminescent imaging)
- Tumor implantation: orthotopic implantation by stereotactic intracranial inoculation
- Standards: temozolomide, doxorubicin, immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-CTLA4, PD1, PDL1 antibodies)
- Readouts: body weight, tumor size, survival
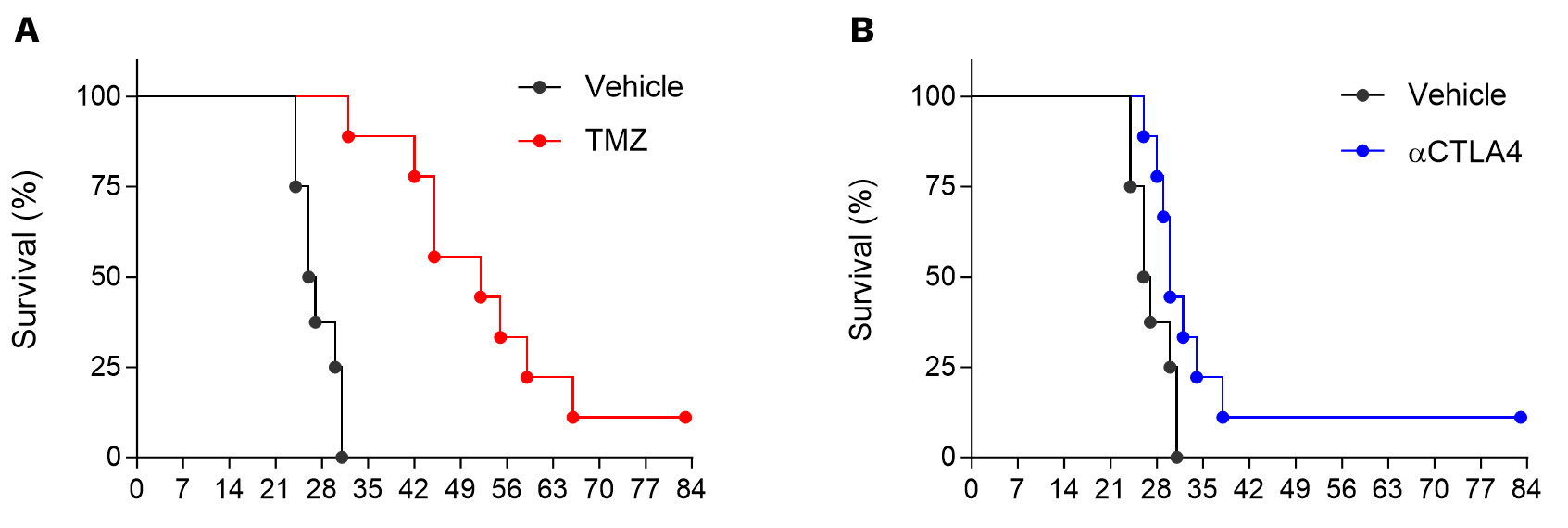
Orthotopic syngeneic GL261 glioblastoma model is strongly responsive to temozolomide (TMZ, A) and moderately to CTLA4 blockade (B).
In vivo efficacy & mechanism of action studies for novel immunotherapies
Straightforward in vivo efficacy studies
- N=10: Standard groups of 10 mice including groups exposed to test compound alone and in combination with reference therapy.
- Weekly reports: monitoring tumor growth, body weight, and survival
Flexible sampling options
- Monitoring response over time: satellite mice, serial bleeding, intra-tumoral biopsies
- On-demand sample collection: blood, serum, plasma, tumor, organ samples
A flexible platform to quantify tumor-microenvironment & peripheral markers
- Multiplex immunophenotyping by flow cytometry & digital pathology
- Spatial transcriptomics & proteomics
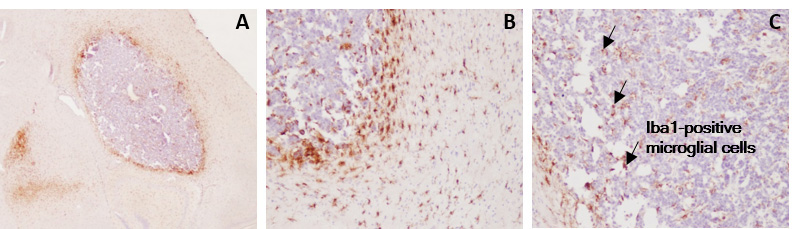
GL261 glioma tumor-bearing model harbors tumor-infiltrating microglial cells.
Immunohistochemistry processing associated with H&E staining highlights the presence of tumor-surrounding (A&B) and tumor-infiltrating (B&C) Iba1-positive microglial cells.
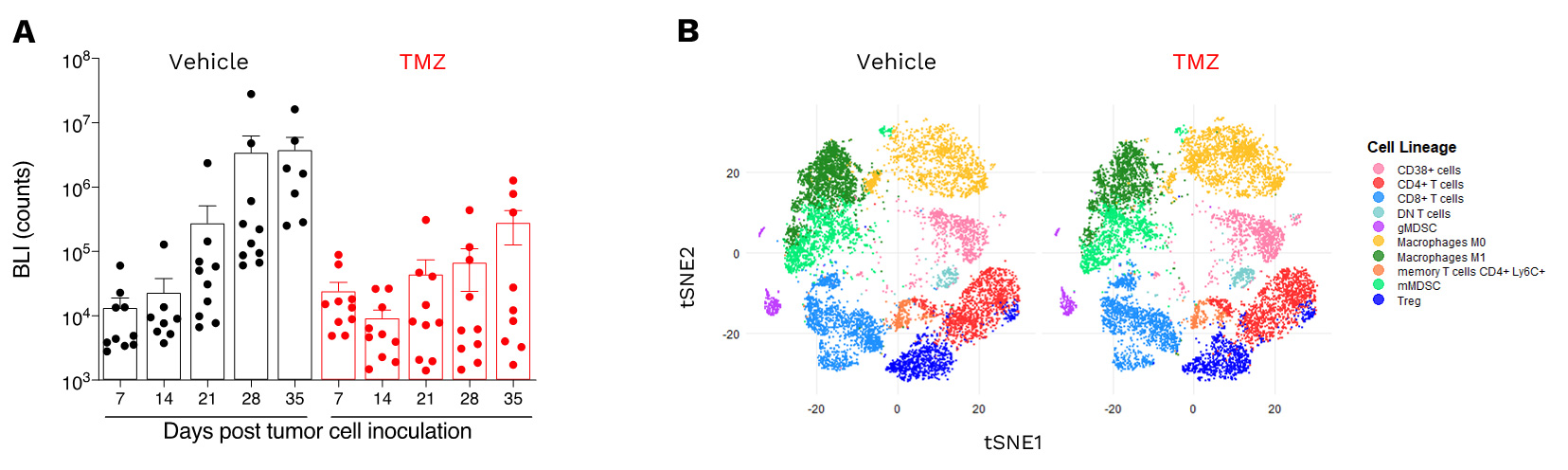
Anti-tumor and immunomodulatory effects of TMZ in the orthotopic syngeneic GL261 glioblastoma model.
A. Orthotopic syngeneic GL261 glioblastoma model responsiveness to TMZ. Mice were OT inoculated with GL261-Luc2 glioma cells and then treated with either vehicle or temozolomide (TMZ). Bioluminescence imaging was performed once a week starting from day7 post-tumor inoculation, on days 7, 14, 21, 28 and 35 post-tumor cell inoculation. B. t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (tSNE) unsupervised clustering plot of single-cell TILs data from orthotopic GL261 tumor model under vehicle or TMZ treatment. tSNE clustering and analysis underlines i) the enriched immune microenvironment of GL261 tumors, as well as ii) differential effects of TMZ on the regulation of immune cell populations, with preferentially a decrease in the gMDSC and M1 macrophage proportions. M1 cell decrease is paralleled to an increase in the proportion of M0 macrophages as well as of CD38-positive cells, suggesting an effect of preventing polarization into potential “dysfunctional” M1 cells, and an increase in some effector or APC cell subsets such as NK or B cells (CD38-expressing cells).
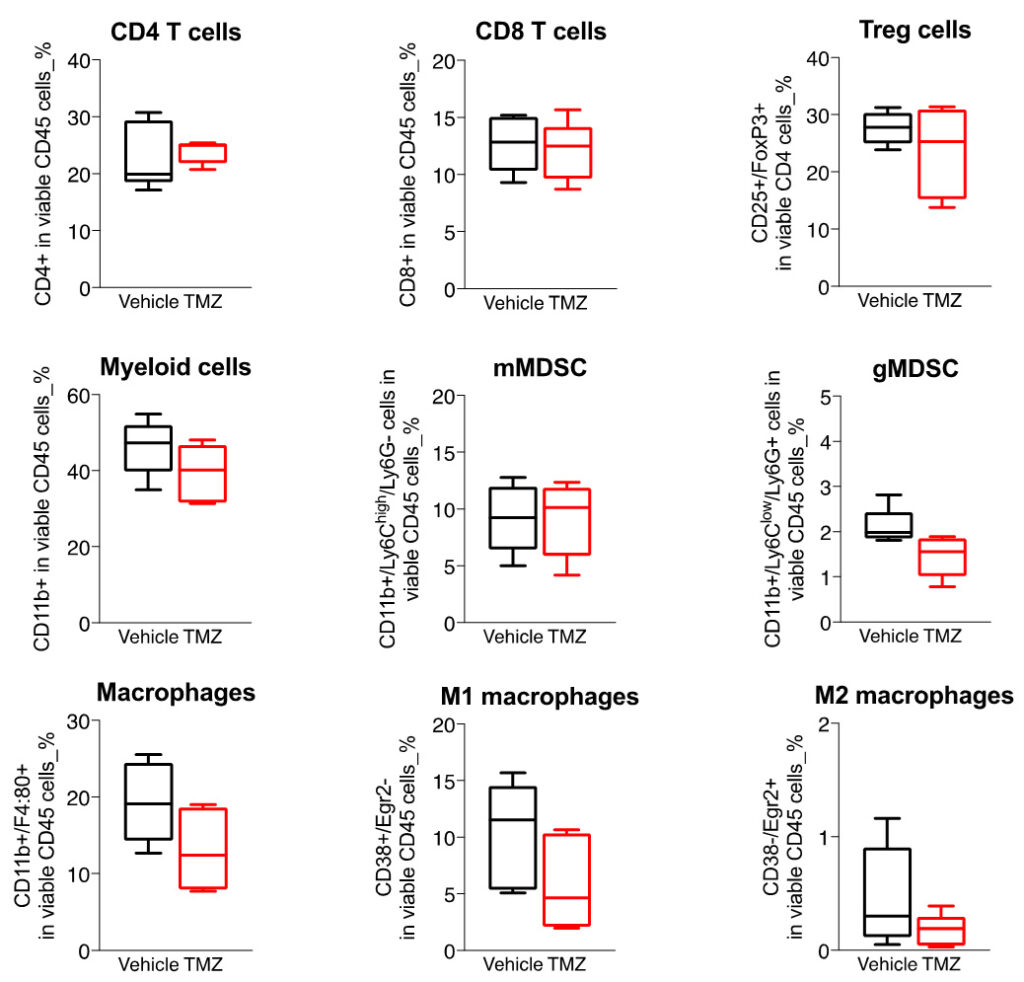
Boxplots of the immune cell populations infiltrating the GL261 tumors in control and TMZ-treated orthotopically-implanted mice.
Flow cytometry analysis of GL261 tumors shows a highly infiltrated tumor microenvironment by both lymphocytic (CD4, CD8, and Treg) subsets) and myeloid cell populations including mainly the immunosuppressive MDSCs as well as macrophages.
Those key immune cell subsets were shown to be differentially modulated upon TMZ treatment – and myeloid cell lineage being preferentially affected; TMZ mainly decreasing gMDSCs as well as macrophages – especially M1 cells, while except a slight decrease tendency in Tregs, no strong changes were observed on T cell components.
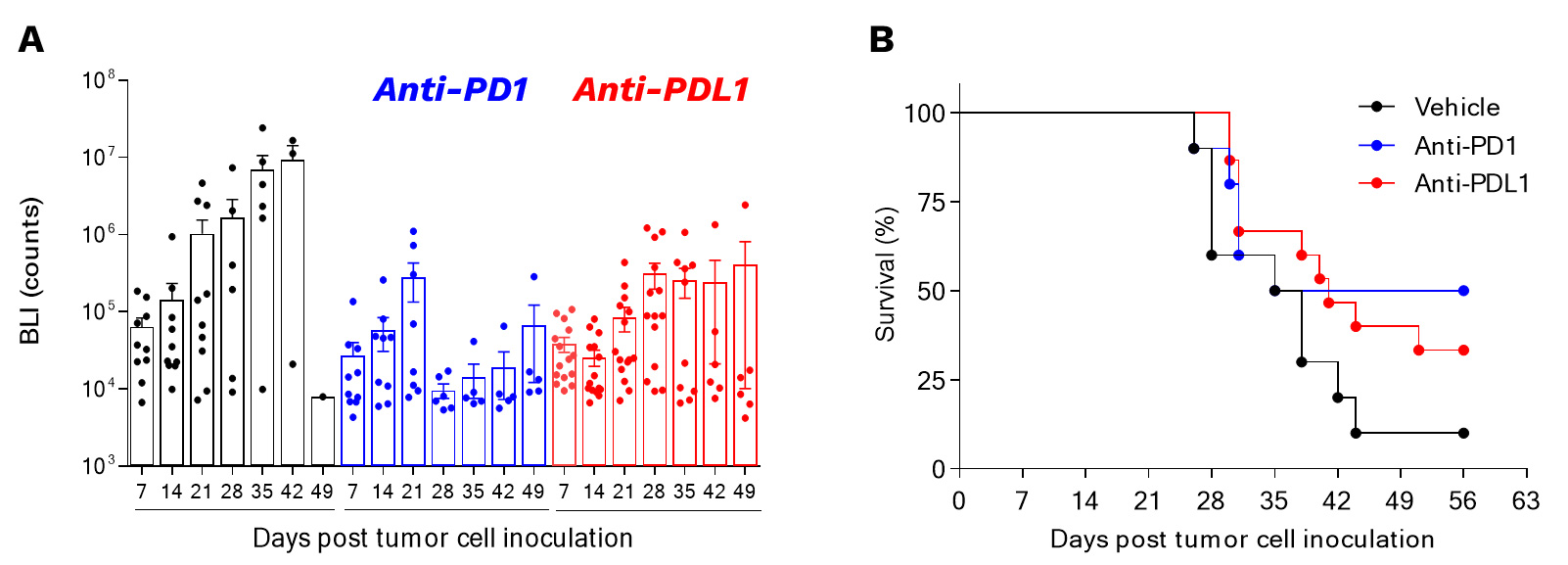
Orthotopic syngeneic GL261 glioblastoma model is responsive to PD1/PDL1 axis blockade.
Mice were orthotopically inoculated with GL261-Luc2 glioma cells and then treated with either Vehicle or anti-PD1 or anti-PDL1 antibodies. Bioluminescence imaging was performed once a week starting from day7 post-tumor inoculation (A), on days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, and 49 post-tumor cell inoculation. Survival was also determined (B).
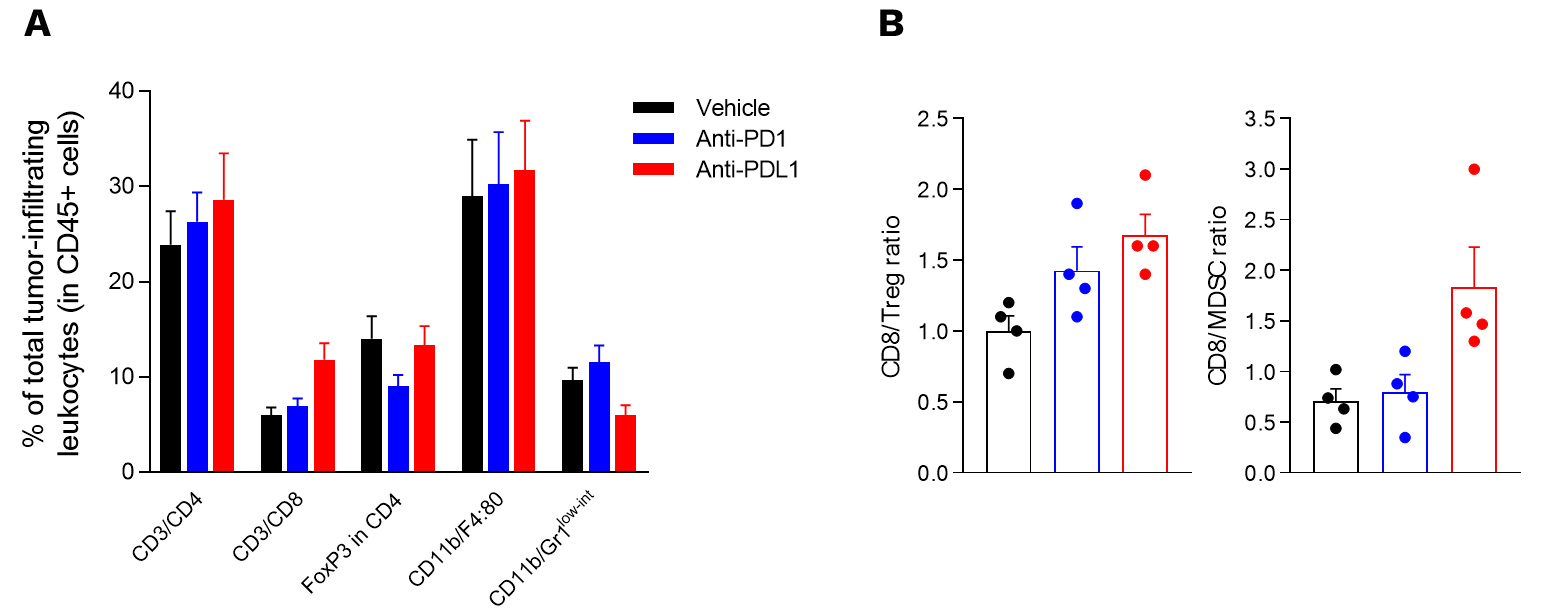
Intracranial glioma tumor-bearing model is characterized by an immunoprivileged microenvironment.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of GL261 tumors shows infiltration by both lymphocytic (CD4, CD8, and Treg (FoxP3+/CD4+) subsets) and myeloid cells including the immunosuppressive MDSC population (CD11b/Gr1low-int).
(A, B) Those key immune cell subsets were shown to be differentially modulated upon treatment with either anti-PD1 or anti-PDL1 antibody – Treg cell population being mainly decreased upon PD1 blockade, while anti-PDL1 antibody was shown to both increase CD8 and decrease MDSC cell infiltration.
Why working with Explicyte?
Experts
in Immuno-Oncology
- 150+ in vivo campaigns conducted over the past 10 years
- 30+ peer-reviewed publications in key immuno-oncology journals
- Bespoke study designs based on client objectives and literature
Personalized
approach
- A dedicated study director (PhD level) from experimental plan to final report
- Weekly reports to provide regular updates & adapt experimental strategy
- Comprehensive analytical platform to decipher anti-tumor response
Your contacts

Talk to our team !
Paul Marteau, PharmD (preclinical study director), Imane Nafia, PhD (CSO), Loïc Cerf, MSc (COO), Alban Bessede, PhD (founder, CEO), Jean-Philippe Guégan, PhD (CTO)
Tell us about your project !
GL261 Syngeneic Mouse Model of Glioblastoma (GL261) I Cancer Immmunotherapy CRO preclinical services
Based on the intracranial implantation of tumors thus closely mimicking human glioblastoma (GBM) with respect to tumor progression and clinical response to tumor growth, our syngeneic glioma tumor-bearing model is a very suitable tool for assessing both in vivo efficacy and MOA of novel therapeutic strategies for brain cancer. Interestingly, this model is run with stable Luc2-expressing GL261 tumor cells which has the advantage to monitor tumor growth and disease progression in vivo by bioluminescence imaging (BLI) along the study. Apart from the advantage of the tumor cells (stably expressing the 2nd generation firefly luciferase) which are intracranially implanted by stereotactic surgery, our syngeneic GBM model mimics the major human disease features including immune cell activation and infiltration, and astrogliosis, among other characteristics. Our syngeneic orthotopic glioblastoma model displays many characteristics which mimic the human disease features and particularly immune cell activation and infiltration. It thus represents a convenient means for both chemotherapy and immunotherapy assessment, and to test drug candidates for their ability to enhance or restore the anti-tumor immune response, in a functionally immunocompetent system. Moreover, our GBM model was set up and validated to assess novel combination regimens with chemotherapy or immunotherapy. Robust treatment protocols combined with validated gold standard chemotherapeutics and immune checkpoint inhibitors have been optimized and allowed to characterize and validate GL261 glioma as responsive to Temozolomide (TMZ) and to anti-CTLA-4 treatment.