The underlying questions: Is your compound capable of switching macrophage polarization from M2 to M1 type, or does it have the potential to relieve M2-mediated immunosuppression?
- Format: adapted miniaturized culture plates
- Models: monocyte-derived M1 or M2 macrophages, alone or in co-culture with autologous activated PBMCs or CD4 T cells
- Readouts:
- T cell activation (IFNγ levels)
- Cytokine release by macrophages (IL6, IL10, IL12)
- Standards: p38 MAPK inhibitor, STAT3 inhibitor, PI3K inhibitor, anti-PD1 (Nivolumab), anti PD-L1 (Atezolizumab), anti-CTLA4 (Ipilimumab)
- On request: Assessment of macrophage and effector immune cytokine release, flow cytometry, immunophenotyping, proteomics, transcriptomics
M1 macrophages
M2 macrophages
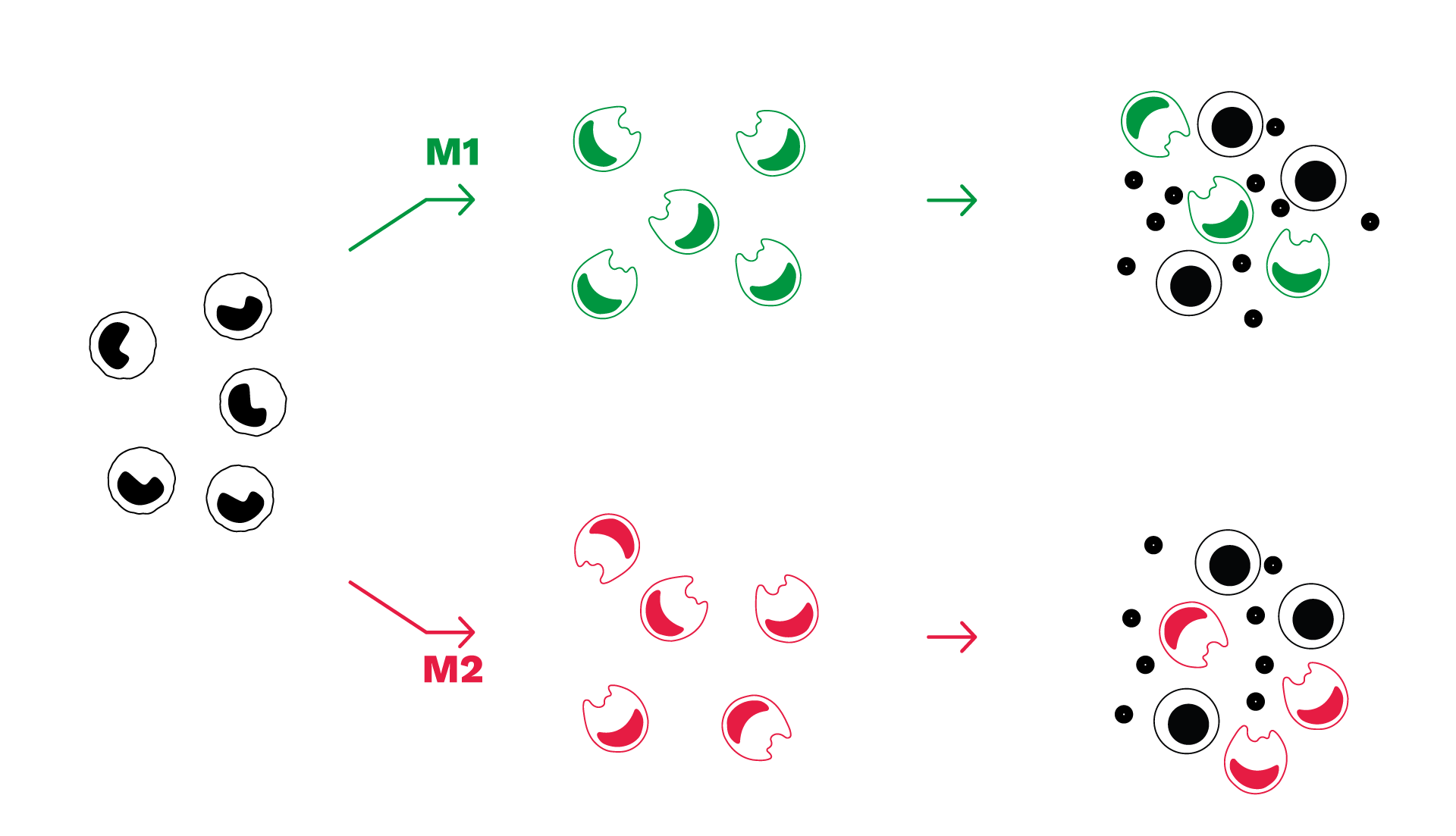
Assay principle
- Our macrophage-based assays – polarization and co-culture assays – are derived from healthy PBMC-isolated monocytes.
- M1 macrophages can be co-cultured with T cells to assess immunotherapies aimed at stimulating macrophage-mediated immune response.
- M2 macrophages can be co-cultured with T cells to assess the capacity of test compound to reverse M2 macrophage-mediated T cell suppression
- Immune cell response is evaluated through the measurement of IFNγ (T cell activation) and cytokines secreted by macrophages (either inflammatory or anti-inflammatory).
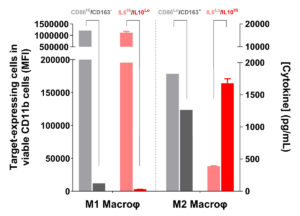
Mirrored phenotypes of marker expression and cytokinic profile feature functionally opposite M1/M2 macrophage subsets.
As functionally distinct subsets, M1 and M2 macrophages exhibit, accordingly, mirrored phenotypic features characterized by IL6High IL10Low and CD86High CD163–, and IL6Low IL10High and CD86Low CD163+ profiles, respectively.
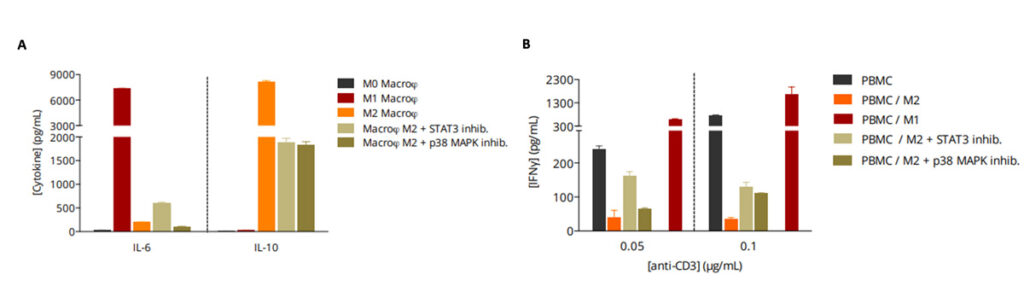
M2 macrophage function is reversed by immunosuppression-mediating pathway inhibitors.
(A) While M2 macrophages display a IL6Low IL10High profile, this latter is implicated in a T cell response suppression known to involve signaling pathways including JAK/STAT and SMAD/p38 MAPK. Indeed, addition of a STAT3 inhibitor or a p38 MAPK inhibitor during the M2 polarization process is shown to be capable of repolarizing/switching M2 phenotype by reversing, at least partially, the IL6Low IL10High profile. (B) Unlike M1 macrophages, which boost T cell activation thereby inducing an increase in IFNg production in PBMC/M1 co-culture, M2 macrophages exhibit a strong suppression of T cell activity shown through IFNg level decrease.
Repolarization/switch of M2 macrophage phenotype, through e.g. STAT3 or p38 MAPK inhibition, prior to their co-cultivation with PBMC, is shown to relieve the immunosuppressive M2 function on T cell response, an effect which occurs subsequently to the reversal of the M2 cytokinic profile.
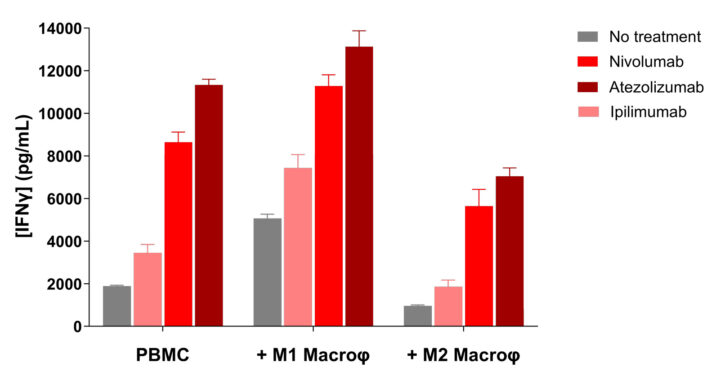
Immune checkpoint blockade antagonizes M2-mediated immunosuppression while promoting M1-mediated immune response stimulation.
Unlike M1 macrophages, which stimulate T cell response thereby inducing an increase in IFNγ production in anti-CD3-activated PBMC/M1 co-culture, M2 macrophages exhibit a suppressive activity of T cell activity shown through IFNγ level decrease.
M2 suppression function is known to be exerted via multiple mechanisms including PD1/PDL1 axis engagement, but also CTLA4/CD80 and CD86. Interestingly, treatments of PBMC/M2 co-cultures with either Nivolumab, Atezolizumab, or even Ipilimumab result in a reversal of the T cell immunosuppression compared to untreated PBMC/M2 co-cultures. On the contrary, these immune checkpoint inhibitors further promote the M1-mediated T cell response stimulation.
Why working with Explicyte?
Experts
in Immuno-Oncology
- 100+ in vitro campaigns conducted over the past 10 years
- 30+ peer-reviewed publications in key immuno-oncology journals
Personalized
approach
- Targeted discussion based on your request to design bespoke strategy & fit-for-purpose study proposal
- A dedicated study director (PhD level) from experimental plan to final report discussion
- A flexible technology platform to decipher your mechanism of action (immune checkpoint activation, signaling pathway, metabolic activity, …)
Your contacts

Talk to our team !
Paul Marteau, PharmD (preclinical study director), Imane Nafia, PhD (CSO), Loïc Cerf, MSc (COO), Alban Bessede, PhD (founder, CEO), Jean-Philippe Guégan, PhD (CTO)
Tell us about your project !
Macrophage assays for immuno-oncology I M1 M2 Polarization I CRO Services
Macrophages – the most abundant antigen-presenting cells in the periphery – represent by themselves a wide group of functionally-different subpopulations involved in several immunological functions, including inflammatory responses and tissue homeostasis maintain & repair. Unlike M1 macrophages which promote a pro-inflammatory response, alternatively activated M2 macrophages, with diametrically opposed functions, trigger inflammation resolution and suppress T cell activation via several mechanisms including immune checkpoint engagement (e.g. PDL1), release of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGFb, and metabolic activities which promote essential amino acid depletion (e.g. Arginine). – which characteristics that they share with the so-called tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Our newly validated M2 suppression assay based on i) the co-culture of autologous monocyte-derived M2 macrophages and activated CD4+ T cells (or PBMCs) and on ii) the quantitation of IFNg levels as surrogate of T cell activation, is specifically designed to assess new immunotherapeutics for their modulatory activity on the phenotype and function of M2 macrophages. Candidate compounds can thus be evaluated as single agents or in combinatorial treatments, for their potential to repolarize / switch M2 macrophages and to antagonize M2-mediated T cell suppression.