-
- Model features: intact immune system, anti-PD1/PD-L1 responding & non-responding tumor models
- Tumor cell line: Breast Cancer (4T1, EMT6), Colon Cancer (CT26, MC38), Gliobastoma (GL261), Lung Cancer (LLC1), Pancreatic cancer (Pan02), Renal Cancer (Renca), Sarcoma (MCA205)
- Tumor implantation: subcutaneous or orthotopic
- Robust treatment protocols using classical well-described antibody clones, in line with published literature data
- Readouts: body weight, tumor size, survival
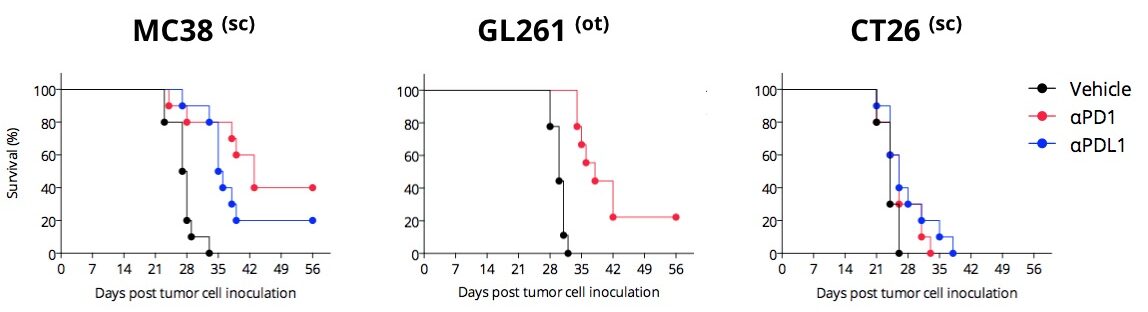
Differential PD1/PDL1 blockade efficacy in different syngeneic mouse models
PD1/PDL1 blockade enhances survival of MC38, moderately that of GL261, but very slightly that of CT26. Mice are challenged with respective tumor cells and exposed to anti-PD1 or anti-PDL1 antibody. In the MC38 responding model, both anti-PD1 and anti-PDL1 antibodies improve mouse survival.
In vivo efficacy & mechanism of action studies for novel immunotherapies
Straightforward in vivo efficacy studies
- N=10: Standard groups of 10 mice including groups exposed to test compound alone and in combination with reference therapy.
- Weekly reports: monitoring tumor growth, body weight, and survival
Flexible sampling options
- Monitoring response over time: satellite mice, serial bleeding, intra-tumoral biopsies
- On-demand sample collection: blood, serum, plasma, tumor, organ samples
A flexible platform to quantify tumor-microenvironment & peripheral markers
- Multiplex immunophenotyping by flow cytometry & digital pathology
- Spatial transcriptomics & proteomics
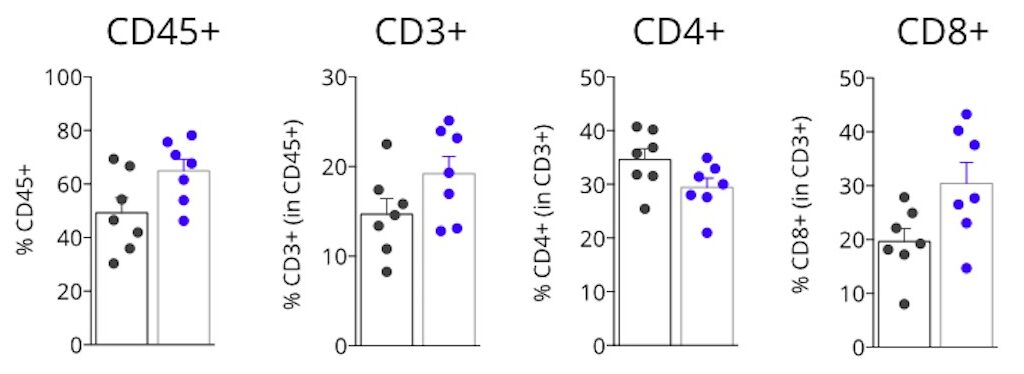
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes profiling of MCA205 tumor-bearing mice upon anti-PDL1 blockade
Flow cytometry analysis of MCA205 tumors highlights a higher immune cell infiltration within the tumor upon PDL1 blockade. Anti-PDL1 antibody treatment of MCA205-timor bearing mice leads to a higher number of Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (CD45+). This feature is associated with an increase in T cells (CD3+) and particularly with an accumulation of effector T cells (CD8+). In contrast, CD4+ T cells infiltration of the tumor is slightly decreased upon treatment.
Why working with Explicyte?
Experts
in Immuno-Oncology
- 150+ in vivo campaigns conducted over the past 10 years
- 20+ peer-reviewed publications in key immuno-oncology journals
- Bespoke study designs based on client objectives and literature
Personalized
approach
- A dedicated study director (PhD level) from experimental plan to final report
- Weekly reports to provide regular updates & adapt experimental strategy
- Comprehensive analytical platform to decipher anti-tumor response
Your contacts

Talk to our team ! Your key contacts:
Study directors: Paul Marteau, PharmD (not on picture), Jean-Philippe Guégan, PhD Leadership: Imane Nafia, PhD (CSO), Alban Bessede, PhD (founder, CEO), Loic Cerf, MSc (COO)
Tell us about your project !
In Vivo Models Of PD-1/PD-L1 Axis Blockade I Cancer Immunotherapy CRO services
While targeting the PD1/PDL1 axis with therapeutic antibodies (eg. nivolumab / atezolizumab) offers unprecedented clinical benefit in metastatic melanoma and lung cancer, durable responses are observed only in a fraction of patients. Current lines of investigations on such therapies mainly aim at evaluating and identifying novel drugs capable of leveraging the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 axis blockade. In this respect, Explicyte offers a range of syngeneic mice models of anti-PD-1 and/or anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy. Furthermore, preclinical efficacy data can be strengthened by ancillary immune cell profiling and MOA studies – relying on key immunological markers quantification, within the tumor or in peripheral organs – thereby allowing a deep interrogation of the immune response elicited by test compounds. Our models can also support for the identification of innovative and novel predictive biomarkers. Combinatory approaches in immuno-oncology with immune checkpoint inhibitors including anti-PD1 / PDL1 or anti-CTLA4 therapeutic antibodies is an active field of investigation. In order to evaluate potential synergistic effect of novel chemotherapeutic agents, immunostimulatory compounds, etc., we characterized the clinical response to anti-PD1 and anti-PDL1 in immunocompetent animal models. Ancillary studies including FACS analysis, RT-qPCR can provide support to delineate mechanism of actions of a drug candidate and can also support the identification of novel predictive biomarkers.